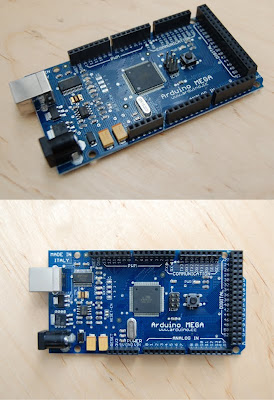
Arduino-Mega
Summary
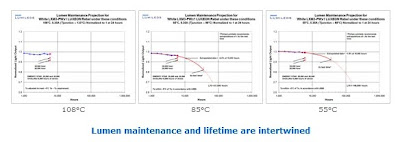
Microcontroller ATmega1280 Operating Voltage 5V Input Voltage (recommended) 7-12V Input Voltage (limits) 6-20V Digital I/O Pins 54 (of which 14 provide PWM output) Analog Input Pins 16 DC Current per I/O Pin 40 mA DC Current for 3.3V Pin 50 mA Flash Memory 128 KB of which 4 KB used by bootloader SRAM 8 KB EEPROM 4 KB Clock Speed 16 MHz Power
The Arduino Mega can be powered via the USB connection or with an external power supply. The power source is selected automatically. External (non-USB) power can come either from an AC-to-DC adapter (wall-wart) or battery. The adapter can be connected by plugging a 2.1mm center-positive plug into the board's power jack. Leads from a battery can be inserted in the Gnd and Vin pin headers of the POWER connector. The board can operate on an external supply of 6 to 20 volts. If supplied with less than 7V, however, the 5V pin may supply less than five volts and the board may be unstable. If using more than 12V, the voltage regulator may overheat and damage the board. The recommended range is 7 to 12 volts.
The power pins are as follows: VIN. The input voltage to the Arduino board when it's using an external power source (as opposed to 5 volts from the USB connection or other regulated power source). You can supply voltage through this pin, or, if supplying voltage via the power jack, access it through this pin. 5V. The regulated power supply used to power the microcontroller and other components on the board. This can come either from VIN via an on-board regulator, or be supplied by USB or another regulated 5V supply. 3V3. A 3.3 volt supply generated by the on-board FTDI chip.
Maximum current draw is 50 mA. GND. Ground pins. Memory The ATmega1280 has 128 KB of flash memory for storing code (of which 4 KB is used for the bootloader), 8 KB of SRAM and 4 KB of EEPROM (which can be read and written with the EEPROM library). Input and Output Each of the 54 digital pins on the Mega can be used as an input or output, using pinMode(), digitalWrite(), and digitalRead() functions. They operate at 5 volts. Each pin can provide or receive a maximum of 40 mA and has an internal pull-up resistor (disconnected by default) of 20-50 kOhms. In addition, some pins have specialized functions: Serial: 0 (RX) and 1 (TX); Serial 1: 19 (RX) and 18 (TX); Serial 2: 17 (RX) and 16 (TX); Serial 3: 15 (RX) and 14 (TX). Used to receive (RX) and transmit (TX) TTL serial data. Pins 0 and 1 are also connected to the corresponding pins of the FTDI USB-to-TTL Serial chip. External Interrupts: 2 (interrupt 0), 3 (interrupt 1), 18 (interrupt 5), 19 (interrupt 4), 20 (interrupt 3), and 21 (interrupt 2).
These pins can be configured to trigger an interrupt on a low value, a rising or falling edge, or a change in value. See the attachInterrupt() function for details. PWM: 0 to 13. Provide 8-bit PWM output with the analogWrite() function. SPI: 50 (MISO), 51 (MOSI), 52 (SCK), 53 (SS). These pins support SPI communication, which, although provided by the underlying hardware, is not currently included in the Arduino language.
The SPI pins are also broken out on the ICSP header, which is physically compatible with the Duemilanove and Diecimila. LED: 13. There is a built-in LED connected to digital pin 13. When the pin is HIGH value, the LED is on, when the pin is LOW, it's off. I2C: 20 (SDA) and 21 (SCL). Support I2C (TWI) communication using the Wire library (documentation on the Wiring website). Note that these pins are not in the same location as the I2C pins on the Duemilanove or Diecimila. The Mega has 16 analog inputs, each of which provide 10 bits of resolution (i.e. 1024 different values). By default they measure from ground to 5 volts, though is it possible to change the upper end of their range using the AREF pin and analogReference() function.
There are a couple of other pins on the board: AREF. Reference voltage for the analog inputs. Used with analogReference(). Reset. Bring this line LOW to reset the microcontroller. Typically used to add a reset button to shields which block the one on the board. Communication The Arduino Mega has a number of facilities for communicating with a computer, another Arduino, or other microcontrollers. The ATmega1280 provides four hardware UARTs for TTL (5V) serial communication. An FTDI FT232RL on the board channels one of these over USB and the FTDI drivers (included with the Arduino software) provide a virtual com port to software on the computer.
The Arduino software includes a serial monitor which allows simple textual data to be sent to and from the Arduino board. The RX and TX LEDs on the board will flash when data is being transmitted via the FTDI chip and USB connection to the computer (but not for serial communication on pins 0 and 1). A SoftwareSerial library allows for serial communication on any of the Mega's digital pins. The ATmega1280 also supports I2C (TWI) and SPI communication. The Arduino software includes a Wire library to simplify use of the I2C bus; see the documentation on the Wiring website for details. To use the SPI communication, please see the ATmega1280 datasheet. Programming The Arduino Mega can be programmed with the Arduino software (download).